GARBAGE COLLECTOR (GC)
Module = A module is a code that can perform an specific
task.
>>> In Python
GC (Garbage Collector) is a module that helps to remove the unwanted objects during
the execution. When a program execution takes place GC generate reference count
to each object. Reference count means how many times the object execute. when
an object has reference count of at least 1 then GC do not removes them but
when an object has reference count of 0 then GC understands that object has not
any use in program and GC removes them.
In the given figure A, B
and C are three object. when we execute this program then Python interpreter
interperate from A object to B object and then execute C after that it passed
to A object. Thus, A, B and C have reference count of 1. So, GC not removes
them.
COMMENT
Observe the given
program :-
The First line of the
given program starts with ‘#’. This
symbol represents comment line. Comment lines are used to describe
the feature of program. It makes the program more understandable (Readable).
When programmers work on big project where more than one people involves then
describing comment becomes very essential because more than 1 people are
involved in programming. So, they all can understands the program are possible
only by describing comments.
>>> Comment is
of two types:-
i) Single line
comments
ii) Multi line comments
➠Single
line comments = this comment
starts with # symbol and do not end till the line changed.
Example :-
➠Multi
line comment = Multi line
comment are the comment which can expand more than one lines.
It is represented by
triple single quote (''' ''') or triple double quote ("""
""").
Example:-
Actually, there is not
any multi line comment; it is just a string value with the exception that it
can expand into multi line. Thus, there is not any multi line comment this is
the string value and it also acquire space in memory. But it is not stored
in any variable and hence, G.C removes them and we can use them as multi line
comment. But many programmer do not use this because it wastes the time of
interpreter.
HOW PYTHON SEES VARIABLES
In other programming
languages like C, Java etc. Variables are connected to memory location. It is
imagined that memory location is just like a storage box in which value is
stored.
For example: - A= 1
When there is a new
value assigned to variables then new value assigned in the storage box and old
value is removed by Garbage Collector (GC).
For example: - A =2
And when a new variable
is assigned in the old variable then a new memory location (storage box) is
created which store the value of the old variable.
For example: - A = B
But in Python, it is
quite different. In Python, Variable is seen as a tag (or name) that is tied to
some value.
For example: - A = 1
Here, there is a value
(1) that is tied by a name 'A'.
When we assigned a new
value to the variable in Python then the new value is tied with the variable
name and old value is removed by G.C.
For example: - A = 2
And when we assigned a
new variable in the old variable then the value of variable is tied with two
variable names.
For example: - A = B
DATATYPE
IN PYTHON
➤Data
type represents the type of data that are stored in variable (or memory).
➧There
are two types of datatype in variable.
i) Built in
datatype
ii) User defined
datatype
⧭Built in datatype are subdividing
into five types:--
⤷ None type
⤷ Numeric type
⤷ Sequence type
⤷ Set type
⤷ Mapping type
➣None
type datatype = this datatype
represents an object which do not contain any value. It is also called Null
datatype.
➣Numeric
datatype = This datatype
represents the number.
There are three sub
types :-
⤷Integer
⤷Float
⤷Complex
➪Integer
datatype = All the integer number
(numeric without fraction or decimal) are represented by Integer datatype.
➪Float
datatype = All the decimal
value are represented by Float datatype.
➪Complex
datatype = The number which are
of the form of a+bj where j = -1^1/2 are called complex number. And all the
complex number is represented by complex datatype.
Example:-
➣Sequence
datatype = Sequence
datatype are the type of datatype which contains the group of element. It is
subdivided into six types:-
⤷ String
⤷ Bytes
⤷ Byte array
⤷ List
⤷ Tuple
⤷ Range
➪String = this datatype are represented by 'str'
and it contains the string value.
Example :-
➪Bytes = this datatype contains the integer value
from 0 to 255 (inclusive). But we cannot do any modification in this data types.
➪Bytearray = This datatype are similar to bytes
datatype. But in this datatype we can do various modifications.
➪List = A list represents a group of elements
and it is denoted by square brackets ([]) and elements are written in square
brackets ([]), separated by commas. For example :-
➪Tuple = A tuple is similar to list and it is
represented by small brackets (). and elements are written in it and
separated by commas.
Example:-
↬ we cannot do any modification in Tuple whereas we can do various
modifications in List datatype.
Example:-
Here, we easily modify the second place value of a list.
But here, we try the same things but we got error due to property of tuple that we can't do any modifications in it.
➪Range = The range datatype represents a sequence
of numbers. The numbers in range are not modifiable. Generally, Range is used
for repeating a for loop for a specific numbers of time. To create a range of
numbers we can take an example:-
Here, The range object
is created with the numbers starting from 0 to 9. we can display these numbers
using a for loop as :-
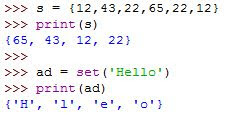
➣Sets
datatype = This datatype
contains a group of elements separated by commas inside the middle braces ({}).
and it doesn't accepts duplicate elements. moreover, order of element is not
maintained in the sets. It means element may not appear in the same order as
they entered into the set.
➧There
are two sub types:-
⤷Set datatype
⤷Frozenset datatype
➭Set
and Frozenset datatype are similar to each other. The only difference is that
in the set datatype we can do modifications whereas frozenset datatype cannot
be modified.
➣Mapping
Type = A map represents
a group of elements in the form of Keys values pair. So, that when the key is
given we can retrieve the value associated with it.
Dict datatype is an example of Map.
➭Dict
datatype = The 'Dict'
represents 'Dictionary' that contains pairs of elements such that the first
element represents the key and next one becomes its value. The key and its
value should be separated by a colon (:) and every pair should be separated by
a comma. All the elements should be enclosed inside curly bracket ({}).
Example:-
##**--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------**##





















Comments
Post a Comment