OPERATORS IN PYTHON
The general purpose of a program is to accept data and perform some operations on the data. The data in the program is stored in variables. The next question is how to perform operations on the data. For example, when a programmer wants to add two numbers, he simply type '+' symbol. This symbol performs addition operation. Such symbols are called operators.
⇨Operator = An operator is a symbol that performs an operation.
When an operator acts on some variables then it is called operands. Example :- a + b in the given equation '+' operator acts on two operands 'a' and 'b'. If an operator acts on single operands then it is called unary operator. And when an operator acts on two operands then it is called binary operator. And when an operator acts on more than two operands (variable) It is called Tertiary operator.
➠Classifications of Operator --
a) Arthimatic operators
b) Assignment operators
c) Unary minus operators
d) Relational operators
e) Logical operators
f) Boolean operators
g) Bitwise operators
h) Membership operators
i) Identity operators
➥Arthimatic operators
➣There are seven arthimatic operators in python: -
f) Exponent (**) = This operator calculates the exponential power value.
When their is an expression which contains several arthimatic operators. Then we should know that which operator will be work first. Let's see that
step 1)) At first parenthesis () are evaluated.
step 2)) Then Exponentiation.
step 3)) Then Multiplication, division, Modulus, and floor division.
Then Addition and subtraction
step 4)) And then at last Assignment operation is performed.
➢Let's take an example to understand this clearly --
⇒5+(4-2)+8*1000/2%9**2//5
⇒5+(4-2)+8*1000/2%9**2//5
⇒5+2+8*1000/2%9**2//5
⇒5+2+8*1000/2%81//5
⇒5+2+8*500%81//5
⇒5+2+8*14//5
⇒5+2+900//5 (8**14 gives huge number so we assume it as 900)
⇒5+2+180
⇒187
➢There are eight types of assignment operators:-
a) Assignment operator (=)
b) Addition assignment operator (+=)
Here, a += 10 means
means a = a+10
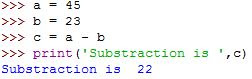
c) Subtraction assignment operator (-=)
Here, a -= 30
means a = a - 30
d) Multiplication assignment operator (*=)
Here, a *= 3
means a = a *3
e) Division assignment operator (/=)
Here, a /= 50
means a = a/50
f) Modulus assignment operator (%=)
Here, a %= 7
means a = a % 7
g) Exponentiation assignment operator (**=)
Here, a **= 3
means a = a **3
h) Floor division assignment operator (//=)
Here, a //= 3
means a = a // 3
➢There are six types of Relational operator :-
a) Greater than operator (>)
b) Greater than or equal to operator (>=)
c) Lesser than operator (<)
d) Lesser than or equal to operator (<=)
e) Equals operator (==)
f) Not equals operator (!=)
Example = num1 and num2
➣Here, When num1 and num2 both condition becomes True then the statements related to it execute.
If only one of them becomes True and other becomes False then the statements related to it not execute.
Program -
b) OR operator
Example = n1 or n2
➣ Here, When n1 or n2, only one condition becomes true then the Statements related to it execute. Otherwise when both of the statements becomes true or false then the statements related to it does not execute.
Program -
c) NOT operator
Example = n1 Not n2
➣Here, When n1 and n2 return False then condition related to it is executed then it executed the statements related to it. When one of them condition return True then the statements related to it don't executed.
***----------------------------------------------------***
I will discuss next types of Operators in next Post..
You can Comment your quiery in the comment Box I will Definitely Solve your quiery and gives reply to your quiry.
➥Assignment Operators
This operator helps to store (or assign) a value into a variable.➢There are eight types of assignment operators:-
a) Assignment operator (=)
b) Addition assignment operator (+=)
Here, a += 10 means
means a = a+10
c) Subtraction assignment operator (-=)
Here, a -= 30
means a = a - 30
d) Multiplication assignment operator (*=)
Here, a *= 3
means a = a *3
e) Division assignment operator (/=)
Here, a /= 50
means a = a/50
f) Modulus assignment operator (%=)
Here, a %= 7
means a = a % 7
g) Exponentiation assignment operator (**=)
Here, a **= 3
means a = a **3
h) Floor division assignment operator (//=)
Here, a //= 3
means a = a // 3
➥Unary Minus Operator
You can understand this by the following example :-➥Relational operator
This operator are use to compare two or more objects.➢There are six types of Relational operator :-
a) Greater than operator (>)
b) Greater than or equal to operator (>=)
c) Lesser than operator (<)
d) Lesser than or equal to operator (<=)
e) Equals operator (==)
f) Not equals operator (!=)
➥Boolean Operator
a) AND operatorExample = num1 and num2
➣Here, When num1 and num2 both condition becomes True then the statements related to it execute.
If only one of them becomes True and other becomes False then the statements related to it not execute.
Program -
b) OR operator
Example = n1 or n2
➣ Here, When n1 or n2, only one condition becomes true then the Statements related to it execute. Otherwise when both of the statements becomes true or false then the statements related to it does not execute.
Program -
c) NOT operator
Example = n1 Not n2
➣Here, When n1 and n2 return False then condition related to it is executed then it executed the statements related to it. When one of them condition return True then the statements related to it don't executed.
***----------------------------------------------------***
I will discuss next types of Operators in next Post..
You can Comment your quiery in the comment Box I will Definitely Solve your quiery and gives reply to your quiry.


























Comments
Post a Comment